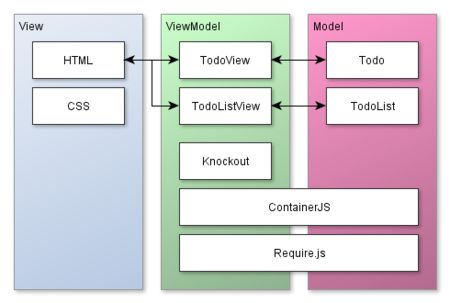
Knockout + ContainerJS でテスタブルにToDoリストを作るチュートリアル
Knockout + ContainerJS + Require.js で テスタブル にToDoリストを作るチュートリアルです。
ポイント
- MVVMアーキテクチャでテスタブルに
- オブジェクトの生成と依存関係を、DIコンテナで一元管理
- JavaScriptソースはクラスごとに分割管理
- 1ファイル200行超えたらメンテナンスとか無理ですよね! ということで、ソースファイルはクラスごとに分割管理します。
- ソース間の依存関係解決と読み込みはrequire.jsで。
- リリース時には、必要なソースをminify && 1ファイルに結合して読み込みを最適化します。
目次
- Modelを作る
- Modelをテストする
- ViewModelを作る
- ViewModelをテストする
- View(HTML/CSS)を作る
- minify && 結合してリリース
ソースはこちらで公開しています。細かいところは省略していたりするので、ソースも合わせて参照ください。
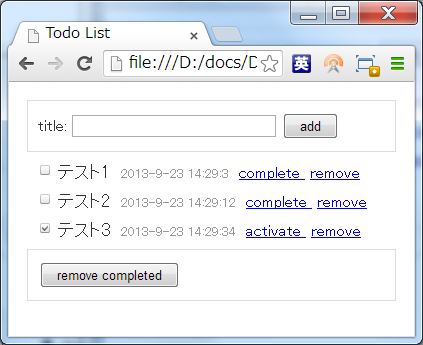
Todoリストの仕様
作成するTodoリストの機能は以下。
- タイトルを入力して、Todoを登録できる。
- Todoにはタイトルと完了したかどうか、作成日、最終更新日の属性がある。
- 終了したTodoは「完了」にできる。
- 完了したものを未完了に戻すこともできる。
- Todoを個別に削除できる。
- 完了したTodoはまとめて削除できる。
TodoMVC で作られているものと大体同じはず。UIは以下のような感じで。
なお、本来は登録したTodoをサーバーに送って保存とか必要ですが、今回はJavaScriptプロジェクトのサンプルということでサーバーとの連携部分は省略します。サーバーで永続化する場合は、Model側のAPI呼び出し時にREST APIなりなんなりを呼び出すようにすればOK。
1. Modelを作る
まずは、Modelを作ります。
- クラスは、TodoとTodoリスト(登録されたTodoの集まりを表すもの)の二つ。
- モデルはPlainなJavaScriptクラスとして定義します。
- フレームワーク(or ライブラリ)依存にはしない派。
- 理由は、このあたり を参照。
- テスタブルで変化に強いモデルにするためには、PlainなJavaScriptクラスにしておくべきと思うのです。
Todo
- タイトル(title),完了したかどうか(completed)、作成日(createdAt)、最終更新日(lastModified)の属性を持ちます。
- タイトルは100文字まで。空文字も不可。
- 各種属性の変更を通知する仕組みを持ちます。(Observerパターン)
- 完了にする(complete)/未完了に戻す(activate)操作ができます。
- 現在時刻はTimeSourceから取得するようにしています。
- 現在時刻に依存しないテストにするためのワンポイント。
- テスト時にはTimeSourceをモックに差し替えて、テスト内での時間をコントロールします。
define([ "models/events", "utils/observable" ], function(Events, Observable){ "use strict"; var sequence = 1; /** * @class */ var Todo = function(timeSource) { Observable.apply(this, arguments); var now = timeSource.now(); this.id = sequence++; this.title = ""; this.completed = false; this.createdAt = now; this.lastModified = now; this.timeSource = timeSource; this.todoList = null; Object.seal(this); }; Todo.prototype = new Observable(); /** * @public * @return {string} */ Todo.prototype.setTitle = function( title ) { validateTitle(title); update(this, "title", title); update(this, "lastModified", this.timeSource.now()); }; /** * @public */ Todo.prototype.complete = function() { update(this, "completed", true); update(this, "lastModified", this.timeSource.now()); }; /** * @public */ Todo.prototype.activate = function() { update(this, "completed", false); update(this, "lastModified", this.timeSource.now()); }; /** * @public */ Todo.prototype.remove = function() { if (!this.todoList) throw new Error("illegal state. todoList is not set."); this.todoList.removeById( this.id ); }; /** @private */ Todo.prototype.attachTo = function( todoList ) { this.todoList = todoList; }; /** * @public * @param {TimeSource} timeSource * @param {string} title * @param {boolean?} completed * @param {Date?} createdAt * @param {Date?} lastModified */ Todo.create = function( timeSource, title, completed, createdAt, lastModified ) { validateTitle(title); var now = timeSource.now(); var todo = new Todo(timeSource); todo.title = title; todo.completed = completed || false; todo.createdAt = createdAt || now; todo.lastModified = lastModified || now; return todo; }; /** @private */ var update = function(that, propertyName, newValue) { var oldValue = that[propertyName]; that[propertyName] = newValue; that.fire(Events.UPDATED, { propertyName : propertyName, newValue : newValue, oldValue : oldValue }); }; /** @private */ var validateTitle = function(title) { if (!title) throw new Error("title is not set."); if (title.length > 100) throw new Error("title is too long."); }; return Object.freeze(Todo); });
TodoList
- Todoの配列(items)と、それを操作するメソッド(Todoの追加や削除)を持ちます。
- Todoと同じく、こちらもObserverパターンでTodoの追加/削除を通知する仕組みを用意。
define([ "container", "models/events", "models/todo", "utils/observable" ], function(ContainerJS, Events, Todo, Observable){ "use strict"; /** * @class */ var TodoList = function() { Observable.apply(this, arguments); this.timeSource = ContainerJS.Inject; this.items = []; Object.seal(this); }; TodoList.prototype = new Observable(); /** * @public */ TodoList.prototype.load = function( ) { this.fire( Events.LOADED, { items: this.items }); }; /** * @public * @param {string} title * @return {Todo} */ TodoList.prototype.add = function( title ) { var todo = Todo.create(this.timeSource, title); todo.attachTo(this); this.items.push(todo); this.fire( Events.ADDED, { added : [todo], items : this.items }); return todo; }; /** * @public */ TodoList.prototype.removeCompleted = function() { removeItems( this, function(item){ return item.completed; }); }; /** * @public * @param {number} id */ TodoList.prototype.removeById = function(id) { removeItems( this, function(item){ return item.id === id; }); }; /** @private */ var removeItems = function( that, f ) { var removed = []; that.items = that.items.filter(function(item){ if (f(item)) { removed.push(item); return false; } else { return true; } }); if (removed.length > 0) { that.fire( Events.REMOVED, { items : that.items, removed: removed }); } }; return Object.freeze(TodoList); });
2. Modelをテストする
Modelができたので、テストを書きます。
Todo spec
define([ "models/todo", "models/events", "test/mock/models/time-source" ], function( Todo, Events, TimeSource ) { describe('Todo', function() { var timeSource = new TimeSource(); timeSource.set(2013, 1, 1); it( "'new' creates a new instance.", function() { var todo = new Todo(timeSource); expect( todo.title ).toEqual( "" ); expect( todo.completed ).toEqual( false ); expect( todo.createdAt ).toEqual( new Date(2013,0,1) ); expect( todo.lastModified ).toEqual( new Date(2013,0,1) ); }); it( "'Todo.create' can creates a new instance with specified properties.", function() { var todo = Todo.create(timeSource, "title", true, new Date(1000), new Date(2000) ); expect( todo.title ).toEqual( "title" ); expect( todo.completed ).toEqual( true ); expect( todo.createdAt ).toEqual( new Date(1000) ); expect( todo.lastModified ).toEqual( new Date(2000) ); todo = Todo.create(timeSource, "title2", false, new Date(2000), new Date(3000) ); expect( todo.title ).toEqual( "title2" ); expect( todo.completed ).toEqual( false ); expect( todo.createdAt ).toEqual( new Date(2000) ); expect( todo.lastModified ).toEqual( new Date(3000) ); }); it( "'setTitle' can updates a title and fire updated events.", function() { var todo = Todo.create(timeSource, "title", false, new Date(1000), new Date(2000) ); var events = []; todo.addObserver( Events.UPDATED, function(ev) { events.push( ev ); }); todo.setTitle("title2"); expect( todo.title ).toEqual( "title2" ); expect( todo.completed ).toEqual( false ); expect( todo.createdAt ).toEqual( new Date(1000) ); expect( todo.lastModified ).not.toEqual( new Date(2000) ); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 2 ); expect( events[0].eventId ).toEqual( Events.UPDATED ); expect( events[0].propertyName ).toEqual( "title" ); expect( events[0].newValue ).toEqual( "title2" ); expect( events[0].oldValue ).toEqual( "title" ); expect( events[1].eventId ).toEqual( Events.UPDATED ); expect( events[1].propertyName ).toEqual( "lastModified" ); expect( events[1].newValue ).toEqual( todo.lastModified ); expect( events[1].oldValue ).toEqual( new Date(2000) ); }); it( "'complete' can updates a completed state and fire updated events.", function() { var todo = Todo.create(timeSource, "title", false, new Date(1000), new Date(2000) ); var events = []; todo.addObserver( Events.UPDATED, function(ev) { events.push( ev ); }); todo.complete(); expect( todo.title ).toEqual( "title" ); expect( todo.completed ).toEqual( true ); expect( todo.createdAt ).toEqual( new Date(1000) ); expect( todo.lastModified ).not.toEqual( new Date(2000) ); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 2 ); expect( events[0].eventId ).toEqual( Events.UPDATED ); expect( events[0].propertyName ).toEqual( "completed" ); expect( events[0].newValue ).toEqual( true ); expect( events[0].oldValue ).toEqual( false ); expect( events[1].eventId ).toEqual( Events.UPDATED ); expect( events[1].propertyName ).toEqual( "lastModified" ); expect( events[1].newValue ).toEqual( todo.lastModified ); expect( events[1].oldValue ).toEqual( new Date(2000) ); }); it( "'activate' can updates a completed state and fire updated events.", function() { var todo = Todo.create(timeSource, "title", true, new Date(1000), new Date(2000) ); var events = []; todo.addObserver( Events.UPDATED, function(ev) { events.push( ev ); }); todo.activate(); expect( todo.title ).toEqual( "title" ); expect( todo.completed ).toEqual( false ); expect( todo.createdAt ).toEqual( new Date(1000) ); expect( todo.lastModified ).not.toEqual( new Date(2000) ); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 2 ); expect( events[0].eventId ).toEqual( Events.UPDATED ); expect( events[0].propertyName ).toEqual( "completed" ); expect( events[0].newValue ).toEqual( false ); expect( events[0].oldValue ).toEqual( true ); expect( events[1].eventId ).toEqual( Events.UPDATED ); expect( events[1].propertyName ).toEqual( "lastModified" ); expect( events[1].newValue ).toEqual( todo.lastModified ); expect( events[1].oldValue ).toEqual( new Date(2000) ); }); }); });
TodoList spec
define([ "models/todo-list", "models/events", "test/mock/models/time-source" ], function( TodoList, Events, TimeSource ) { describe('TodoList', function() { var todoList; var events = []; beforeEach(function() { todoList = new TodoList(); todoList.timeSource = new TimeSource(); [Events.LOADED,Events.ADDED,Events.REMOVED].forEach(function(i) { todoList.addObserver( i, function(ev) { events.push( ev ); }); }); }); afterEach(function() { events = []; }); it( "'add' creates and add a new todo.", function() { todoList.add("test1"); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[0].eventId ).toEqual( Events.ADDED ); expect( events[0].added.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[0].added[0].title ).toEqual( "test1" ); expect( events[0].items.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[0].items[0].title ).toEqual( "test1" ); todoList.add("test2"); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 2 ); expect( events[1].eventId ).toEqual( Events.ADDED ); expect( events[1].added.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[1].added[0].title ).toEqual( "test2" ); expect( events[1].items.length ).toEqual( 2 ); expect( events[1].items[0].title ).toEqual( "test1" ); expect( events[1].items[1].title ).toEqual( "test2" ); }); it( "'removeById' removes todos by id.", function() { var items = []; items.push(todoList.add("test1")); items.push(todoList.add("test2")); items.push(todoList.add("test3")); expect( todoList.items.length ).toEqual( 3 ); events = []; todoList.removeById( items[1].id ); { expect( todoList.items.length ).toEqual( 2 ); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[0].eventId ).toEqual( Events.REMOVED ); expect( events[0].removed.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[0].removed[0].title ).toEqual( "test2" ); expect( events[0].items.length ).toEqual( 2 ); expect( events[0].items[0].title ).toEqual( "test1" ); expect( events[0].items[1].title ).toEqual( "test3" ); } todoList.removeById( items[2].id ); { expect( todoList.items.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 2 ); expect( events[1].eventId ).toEqual( Events.REMOVED ); expect( events[1].removed.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[1].removed[0].title ).toEqual( "test3" ); expect( events[1].items.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[1].items[0].title ).toEqual( "test1" ); } todoList.removeById( 9999 ); { expect( todoList.items.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 2 ); } todoList.removeById( items[0].id ); { expect( todoList.items.length ).toEqual( 0 ); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 3 ); expect( events[2].eventId ).toEqual( Events.REMOVED ); expect( events[2].removed.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[2].removed[0].title ).toEqual( "test1" ); expect( events[2].items.length ).toEqual( 0 ); } }); it( "'removeCompleted' removes completed todos.", function() { var items = []; items.push(todoList.add("test1")); items.push(todoList.add("test2")); items.push(todoList.add("test3")); expect( todoList.items.length ).toEqual( 3 ); events = []; todoList.removeCompleted( ); { expect( todoList.items.length ).toEqual( 3 ); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 0 ); } items[1].complete(); items[2].complete(); todoList.removeCompleted( ); { expect( todoList.items.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[0].eventId ).toEqual( Events.REMOVED ); expect( events[0].removed.length ).toEqual( 2 ); expect( events[0].removed[0].title ).toEqual( "test2" ); expect( events[0].removed[1].title ).toEqual( "test3" ); expect( events[0].items.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[0].items[0].title ).toEqual( "test1" ); } items[0].complete(); todoList.removeCompleted( ); { expect( todoList.items.length ).toEqual( 0 ); expect( events.length ).toEqual( 2 ); expect( events[1].eventId ).toEqual( Events.REMOVED ); expect( events[1].removed.length ).toEqual( 1 ); expect( events[1].removed[0].title ).toEqual( "test1" ); expect( events[1].items.length ).toEqual( 0 ); } }); }); });
テストが書けたら、実行環境を整備していきます。
の2つを用意。
HTML版
Jasminのテストランナーをベースに作成します。ファイル構成は以下。
├src/ │└models/ │ ├todo.js │ └todo-list.js └ test/ ├specs/ .. テストを格納するディレクトリ │└models/ │ ├todo.js │ └todo-list.js ├all-specs.js ├config.js .. テスト用のrequire.js設定ファイル └test.html .. テストをブラウザ上で実行する時に読み込ませるHTMLファイル
test.htmlは以下の内容。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Jasmine Test Runner</title> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="../../../lib-test/jasmine-1.0.2/jasmine.css"> <script type="text/javascript" src="../../../lib/require.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="config.js"></script> </head> <body> <script type="text/javascript"> require(["jasmine/jasmine"], function() { require(["jasmine/jasmine-html","larrymyers-jasmine-reporters/jasmine.console_reporter"], function() { require(["test/all-specs"], function() { jasmine.getEnv().addReporter(new jasmine.TrivialReporter()); jasmine.getEnv().execute(); }); }); }); </script> </body> </html>
config.jsにrequire.jsの設定を書きます。pathsに依存モジュールのパスを設定。
require.config({ baseUrl: "../src/js", paths: { "container" : "../../../../minified/container", "knockout" : "./knockout-2.3.0", "test" : "../../test", "jasmine" : "../../../../lib-test/jasmine-1.0.2", "larrymyers-jasmine-reporters" : "../../../../lib-test/larrymyers-jasmine-reporters-adf6227/src" }, waitSeconds: 1 });
all-specs.js でテストを読み込みます。
define([ "test/specs/models/todo", "test/specs/models/todo-list" ]);
あとは、test.htmlをブラウザにドラッグ&ドロップすれば、テストが実行されるはず。
コマンドライン版
Antを使います。 javaタスクでRhinoからテストを実行します。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project name="todo lists" default="release" basedir="."> <property name="test.dir" value="test" /> <property name="tools.dir" value="../../tools" /> <property name="rhino.home" value="${tools.dir}/rhino1_7R4" /> <property name="jasmine.home" value="../../lib-test/jasmine-1.0.2" /> <property name="jasmine-reporters.home" value="../../lib-test/larrymyers-jasmine-reporters-adf6227" /> <property name="envjs.home" value="../../lib-test/thatcher-env-js-cb738b9" /> <property name="closure-compiler.home" value="${tools.dir}/compiler-20130603" /> <target name="test"> <java jar="${rhino.home}/js.jar" fork='true' dir="test"> <arg line="-encoding utf-8 -opt -1 cui.js"/> <sysproperty key="envjs.home" value="../${envjs.home}"/> </java> </target> </project>
cui.jsの内容は以下。
- Rhinoでテストを実行するための設定をごにょごにょ書いていきます。
- config.js,all-specs.jsはhtml版と共有。
load("../../../tools/r.js"); load("../../../lib/require.js"); load(environment["envjs.home"]+"/dist/env.rhino.js"); load(environment["config"] || "config.js"); console = {}; console.log = function(str) { print(str); }; var consoleReporter = null; require(["jasmine/jasmine"], function() { require(["jasmine/jasmine-html", "larrymyers-jasmine-reporters/jasmine.console_reporter"], function() { require(["test/all-specs"], function() { consoleReporter = new jasmine.ConsoleReporter(); jasmine.getEnv().addReporter( consoleReporter ); jasmine.getEnv().execute(); }); }); }); Envjs.wait(); var filedCount = consoleReporter.executed_specs - consoleReporter.passed_specs; quit(filedCount <= 0 ? 0 : 1);
あとは、
$ ant test
で実行。テストが走ります。
Buildfile: D:\git\container-js\samples\todo-list-example\build.xml
test:
[java] See https://github.com/jrburke/r.js for usage.
[java] [ Envjs/1.6 (Rhino; U; Windows 7 amd64 6.1; en-US; rv:1.7.0.rc2) Resig/20070309 PilotFish/1.2.13 ]
[java] Runner Started.
[java] Todo : 'new' creates a new instance. ...
[java] Passed.
[java] Todo : 'Todo.create' can creates a new instance with specified properties. ...
[java] Passed.
[java] Todo : 'setTitle' can updates a title and fire updated events. ...
[java] Passed.
[java] Todo : 'complete' can updates a completed state and fire updated events. ...
[java] Passed.
[java] Todo : 'activate' can updates a completed state and fire updated events. ...
[java] Passed.
[java] Todo: 51 of 51 passed.
[java] TodoList : 'add' creates and add a new todo. ...
[java] Passed.
[java] TodoList : 'removeById' removes todos by id. ...
[java] Passed.
[java] TodoList : 'removeCompleted' removes completed todos. ...
[java] Passed.
[java] TodoList: 54 of 54 passed.
[java] Runner Finished.
[java] 8 specs, 0 failures in 0.289s.
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 5 seconds
3.ViewModelを作る
Modelの次はViewModelを作っていきます。
- ViewModelは「UI独自の状態や処理を管理するオブジェクト」です。
- Modelをラップする形で、ModelとViewの仲立ちをします。
- Todoリストであれば、以下のような処理がViewModelの担当になります。
- 最終更新日時をUIで表示する文字列に変換する。
- Todoの追加ボタンや、完了したTodoを消すボタン、などの処理を実行するメソッドを提供する。
- 完了したTodoを消すボタンの利用可/不可状態を制御する。(完了したTodoが1つもなければ利用不可)
- Todoを追加する際にタイトルを設定する口を提供する。
- UI依存のロジックをViewModelとして分離することで、Modelはより純粋なビジネスロジックだけを提供する層にできます。
- UIの変更があってもViewModelだけでの変更で済み、Modelには波及しにくくなります。
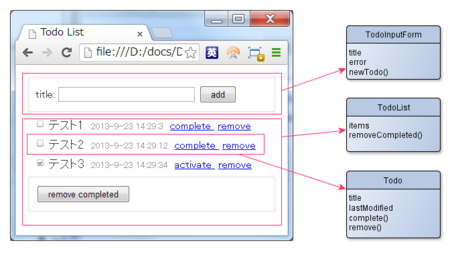
「UIを抽象化してオブジェクトにしたもの」考えるとわかりやすいかも。イメージ的には以下のような感じ。
UIを抽象化したものなので、 実際のUI操作シナリオに沿った形でテストケースが書けるのもポイントです。
作成するViewModelの一覧
作成するViewModelは以下の3つです。
- TodoListView
- Todoの一覧部分に対応するViewModelです。
- TodoView
- Todo一覧の中の各Todoに対応するViewModelです。
- TodoInputForm
- 新しいTodoを作成する入力フォーム部分に対応するViewModelです。
ViewModelではKnockoutの機能を利用します。
TodoListView
- items でTodoの一覧を持ちます。
- itemsはモデルの変更通知を受けて随時更新。
- UI上のボタンを押下した際の処理をメソッドで提供します。
- Todoの追加(newTodo),完了したTodoの削除(removeCompleted)
- enableToRemoveCompleted で完了したTodoの削除ボタンが利用可かどうかを管理します。
define([ "container", "knockout", "models/events", "viewmodels/todo-view" ], function(ContainerJS, ko, Events, TodoView){ "use strict"; /** * @class */ var TodoListView = function() { this.todoList = ContainerJS.Inject; this.todoInputForm = ContainerJS.Inject; this.items = ko.observableArray(); this.numberOfCompleted = ko.observable(0); this.enableToRemoveCompleted = ko.computed(function(){ return this.numberOfCompleted() > 0; }.bind(this)); Object.seal(this); }; TodoListView.prototype.initialize = function(){ this.todoList.addObserver( Events.LOADED, this.onLoad.bind(this) ); this.todoList.addObserver( Events.ADDED, this.onAdded.bind(this) ); this.todoList.addObserver( Events.REMOVED, this.onRemoved.bind(this) ); }; TodoListView.prototype.newTodo = function() { this.todoInputForm.newTodo(); }; TodoListView.prototype.removeCompleted = function(event) { this.todoList.removeCompleted(); }; TodoListView.prototype.onLoad = function(event) { this.items(event.items.map(function(todo){ this.addObserverToTodo(todo); return new TodoView(todo); }.bind(this))); }; TodoListView.prototype.onAdded = function(event) { event.added.forEach( function( todo ) { this.addObserverToTodo(todo); this.updateNumberOfCompleted( todo.completed ? 1 : 0 ); this.items.push(new TodoView(todo)); }.bind(this)); }; TodoListView.prototype.onRemoved = function(event) { var removedIds = {}; event.removed.forEach( function( todo ) { this.updateNumberOfCompleted( todo.completed ? -1 : 0 ); removedIds[todo.id] = true; }.bind(this)); this.items.remove( function(item) { return removedIds[item.model.id]; }); }; /** @private */ TodoListView.prototype.addObserverToTodo = function(todo){ todo.addObserver( Events.UPDATED, this.onTodoUpdated.bind(this)); }; /** @private */ TodoListView.prototype.onTodoUpdated = function(event){ if (event.propertyName === "completed") { if (event.newValue !== event.oldValue) { this.updateNumberOfCompleted( event.newValue ? 1 : -1 ); } } }; /** @private */ TodoListView.prototype.updateNumberOfCompleted = function(count){ this.numberOfCompleted( this.numberOfCompleted()+count ); }; return Object.freeze(TodoListView); });
TodoView
一覧の各Todoに対応するViewModelです。
- タイトル(title)や最終更新時刻(lastModified)などを持ちます。
- Todoの完了操作や、(個別の)削除はTodoごとの操作なので、こちらに定義します。
define([ "container", "knockout", "models/events", "viewmodels/todo-view" ], function(ContainerJS, ko, Events, TodoView){ "use strict"; /** * @class */ var TodoView = function(todo) { this.model = todo; this.title = ko.observable(todo.title); this.completed = ko.observable(todo.completed); this.createdAt = ko.observable(todo.createdAt); this.lastModified = ko.observable(todo.lastModified); this.createdAtForDisplay = ko.computed(function(){ return formatDate(this.createdAt()); }.bind(this)); this.lastModifiedForDisplay = ko.computed(function(){ return formatDate(this.lastModified()); }.bind(this)); this.addObservers(); Object.seal(this); }; TodoView.prototype.addObservers = function(){ this.model.addObserver( Events.UPDATED, this.onUpdated.bind(this) ); }; TodoView.prototype.remove = function() { this.model.remove(); }; TodoView.prototype.complete = function(event) { this.model.complete(); }; TodoView.prototype.activate = function(event) { this.model.activate(); } TodoView.prototype.onUpdated = function(event) { this[event.propertyName](event.newValue); }; var formatDate = function(d){ if (!d) return ""; return d.getFullYear() + "-" + (d.getMonth() + 1) + "-" + d.getDate() + " " + d.getHours() + ":" + d.getMinutes() + ":" + d.getSeconds(); }; return Object.freeze(TodoView); });
TodoInputForm
最後はTodoInputForm。Todoの新規作成フォーム部分に対応するViewModelです。
- タイトル(title)を受け取る口とエラー情報(error)を持ちます。
- Todo追加の本処理もこちらに定義しています。
define([ "container", "knockout" ], function(ContainerJS, ko){ "use strict"; /** * @class */ var TodoInputForm = function() { this.todoList = ContainerJS.Inject; this.title = ko.observable(""); this.titleLength = ko.computed(function(){ return this.title().length; }.bind(this)); this.error = ko.observable(""); Object.seal(this); }; TodoInputForm.prototype.newTodo = function() { try { this.todoList.add( this.title() ); this.title(""); this.error(""); } catch ( exception ) { this.error(exception.message); } }; return Object.freeze(TodoInputForm); });
ViewModelとModelの生成と関連付けはContainerJSで管理します。ContainerJS用のモジュール定義(composing/modules.js)も用意しておきます。
define(["container"], function( ContainerJS ) { "use strict"; var models = function( binder ){ binder.bind("todoList").to("models.TodoList"); binder.bind("timeSource").to("models.TimeSource"); }; var viewmodels = function( binder ){ binder.bind("todoListView").to("viewmodels.TodoListView").onInitialize("initialize"); binder.bind("todoInputForm").to("viewmodels.TodoInputForm"); }; var modules = function( binder ){ models(binder); viewmodels(binder); }; return modules; });
4.ViewModelをテストする
ViewModelもテストしていきます。
- 今回はModelのモックは用意せず、ViewModel+Modelの動きをまとめてテストするようにしました。
- TimeSourceのみmockを使います。
- テストでもViewModel,Modelの作成はContainerJSを使って行います。
TodoListView spec
- Todoの追加・削除が動作することを確認。
- 追加・削除に応じて一覧のデータが増減することもチェック。
define([ "container", "models/events", "test/mock/modules", "test/utils/wait" ], function( ContainerJS, Events, modules, Wait ) { describe('TodoListView', function() { var container; var deferred; beforeEach(function() { container = new ContainerJS.Container( modules ); deferred = container.get( "todoListView" ); }); it( "first, items is empty .", function() { Wait.forFix(deferred); runs( function(){ var view = ContainerJS.utils.Deferred.unpack( deferred ); view.todoList.load(); expect( view.items().length ).toBe( 0 ); }); }); it( "can adds a new todo.", function() { Wait.forFix(deferred); runs( function(){ var view = ContainerJS.utils.Deferred.unpack( deferred ); view.todoList.load(); view.todoInputForm.title("test"); view.newTodo(); view.todoInputForm.title("test2"); view.newTodo(); view.todoInputForm.title("test3"); view.newTodo(); expect( view.items().length ).toBe( 3 ); expect( view.items()[0].title() ).toBe( "test" ); expect( view.items()[1].title() ).toBe( "test2" ); expect( view.items()[2].title() ).toBe( "test3" ); }); }); it( "can removes a todo.", function() { Wait.forFix(deferred); runs( function(){ var view = ContainerJS.utils.Deferred.unpack( deferred ); view.todoList.load(); view.todoInputForm.title("test"); view.newTodo(); view.todoInputForm.title("test2"); view.newTodo(); view.todoInputForm.title("test3"); view.newTodo(); expect( view.items().length ).toBe( 3 ); expect( view.items()[0].title() ).toBe( "test" ); expect( view.items()[1].title() ).toBe( "test2" ); expect( view.items()[2].title() ).toBe( "test3" ); view.items()[1].remove(); expect( view.items().length ).toBe( 2 ); expect( view.items()[0].title() ).toBe( "test" ); expect( view.items()[1].title() ).toBe( "test3" ); }); }); it( "can removes completed todos.", function() { Wait.forFix(deferred); runs( function(){ var view = ContainerJS.utils.Deferred.unpack( deferred ); view.todoList.load(); expect( view.enableToRemoveCompleted() ).toBe( false ); view.todoInputForm.title("test"); view.newTodo(); view.todoInputForm.title("test2"); view.newTodo(); view.todoInputForm.title("test3"); view.newTodo(); expect( view.items().length ).toBe( 3 ); expect( view.items()[0].title() ).toBe( "test" ); expect( view.items()[1].title() ).toBe( "test2" ); expect( view.items()[2].title() ).toBe( "test3" ); expect( view.enableToRemoveCompleted() ).toBe( false ); view.items()[0].complete(); expect( view.enableToRemoveCompleted() ).toBe( true ); view.items()[2].complete(); expect( view.enableToRemoveCompleted() ).toBe( true ); view.removeCompleted(); expect( view.items().length ).toBe( 1 ); expect( view.items()[0].title() ).toBe( "test2" ); expect( view.enableToRemoveCompleted() ).toBe( false ); view.items()[0].complete(); expect( view.enableToRemoveCompleted() ).toBe( true ); view.items()[0].activate(); expect( view.enableToRemoveCompleted() ).toBe( false ); }); }); }); });
TodoView spec
- Todoモデルのプロパティが正しく反映されていることを確認。
define([ "models/todo", "models/events", "viewmodels/todo-view", "test/mock/models/time-source" ], function( Todo, Events, TodoView, TimeSource ) { describe('TodoView', function() { var timeSource = new TimeSource(); beforeEach(function() { timeSource.set(2013, 1, 1); }); it( "reflects a model's value.", function() { var todo = new Todo(timeSource); todo.setTitle("test."); var view = new TodoView(todo); { expect( view.title() ).toBe( "test." ); expect( view.completed() ).toBe( false ); expect( view.createdAt() ).toEqual( new Date( 2013, 0, 1 ) ); expect( view.lastModified() ).toEqual( new Date( 2013, 0, 1 )); expect( view.createdAtForDisplay() ).toEqual( "2013-1-1 0:0:0" ); expect( view.lastModifiedForDisplay() ).toEqual( "2013-1-1 0:0:0" ); } timeSource.set(2013, 2, 10); todo.setTitle("test2."); { expect( view.title() ).toBe( "test2." ); expect( view.completed() ).toBe( false ); expect( view.createdAt() ).toEqual( new Date( 2013, 0, 1 ) ); expect( view.lastModified() ).toEqual( new Date( 2013, 1, 10 )); expect( view.createdAtForDisplay() ).toEqual( "2013-1-1 0:0:0" ); expect( view.lastModifiedForDisplay() ).toEqual( "2013-2-10 0:0:0" ); } timeSource.set(2013, 2, 12); todo.complete(); { expect( view.title() ).toBe( "test2." ); expect( view.completed() ).toBe( true ); expect( view.createdAt() ).toEqual( new Date( 2013, 0, 1 ) ); expect( view.lastModified() ).toEqual( new Date( 2013, 1, 12 )); expect( view.createdAtForDisplay() ).toEqual( "2013-1-1 0:0:0" ); expect( view.lastModifiedForDisplay() ).toEqual( "2013-2-12 0:0:0" ); } timeSource.set(2013, 3, 7); todo.activate(); { expect( view.title() ).toBe( "test2." ); expect( view.completed() ).toBe( false ); expect( view.createdAt() ).toEqual( new Date( 2013, 0, 1 ) ); expect( view.lastModified() ).toEqual( new Date( 2013, 2, 7 )); expect( view.createdAtForDisplay() ).toEqual( "2013-1-1 0:0:0" ); expect( view.lastModifiedForDisplay() ).toEqual( "2013-3-7 0:0:0" ); } }); }); });
TodoInputForm spec
- タイトルを入れてTodoを追加できる、タイトルが未入力だと追加できずエラーが表示される、といったあたりを確認。
define([ "container", "models/events", "test/mock/modules", "test/utils/wait" ], function( ContainerJS, Events, modules, Wait ) { describe('TodoInputForm', function() { var container; beforeEach(function() { container = new ContainerJS.Container( modules ); }); it( "'newTodo' can create a new Todo.", function() { var deferred = container.get( "todoInputForm" ); Wait.forFix(deferred); runs( function(){ var form = ContainerJS.utils.Deferred.unpack( deferred ); { expect( form.title() ).toBe( "" ); expect( form.titleLength() ).toBe( 0 ); expect( form.error() ).toBe( "" ); expect( form.todoList.items.length ).toBe( 0 ); } form.title("test."); { expect( form.title() ).toBe( "test." ); expect( form.titleLength() ).toBe( 5 ); expect( form.error() ).toBe( "" ); } form.newTodo(); { expect( form.title() ).toBe( "" ); expect( form.titleLength() ).toBe( 0 ); expect( form.error() ).toBe( "" ); expect( form.todoList.items.length ).toBe( 1 ); expect( form.todoList.items[0].title ).toBe( "test." ); } }); }); it( "'newTodo' fails when the title is invalid.", function() { var deferred = container.get( "todoInputForm" ); Wait.forFix(deferred); runs( function(){ var form = ContainerJS.utils.Deferred.unpack( deferred ); form.newTodo(); { expect( form.title() ).toBe( "" ); expect( form.titleLength() ).toBe( 0 ); expect( form.error() ).toBe( "title is not set." ); expect( form.todoList.items.length ).toBe( 0 ); } form.title( createStringOfLength(101) ); form.newTodo(); { expect( form.title() ).toBe( createStringOfLength(101) ); expect( form.titleLength() ).toBe( 101 ); expect( form.error() ).toBe( "title is too long." ); expect( form.todoList.items.length ).toBe( 0 ); } form.title( createStringOfLength(100) ); form.newTodo(); { expect( form.title() ).toBe( "" ); expect( form.titleLength() ).toBe( 0 ); expect( form.error() ).toBe( "" ); expect( form.todoList.items.length ).toBe( 1 ); expect( form.todoList.items[0].title ).toBe( createStringOfLength(100) ); } }); }); var createStringOfLength = function(length) { var str = ""; for ( var i=length;i>0;i-- ) str += "a"; return str; }; }); });
5.View(HTML/CSS)を作る
ModelとViewModelができたら、Viewを作成して、View/ViewModel/Modelを生成する部分のコードを書いていきます。
まずはHTML。
- 「data-bind」でViewとViewModelを繋いでいきます。
- ここにViewModelの○○で保持されるデータを流し込む
- このボタンが押されたら、ViewModelの▲▲メソッドを実行、といった感じ。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Todo List</title> <script type="text/javascript" data-main="../js/main.js" src="../../../../lib/require.js"> </script> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="../css/todo-list.css"> </head> <body> <div class="todo-input-form"> title: <input type="text" data-bind="value:todoInputForm.title" class="title-field"></input> <button data-bind="click:newTodo" class="add-button"> add </button> <div class="error" data-bind="text:todoInputForm.error"></div> </div > <div class="todo-list" data-bind="foreach:items, visible:true" style="display:none;"> <div class="todo"> <img src="../images/normal.png" alt="" data-bind="visible:!completed()" /> <img src="../images/check.png" alt="checked" data-bind="visible:completed" /> <span class="title" data-bind="text:title"></span> <span class="last-modified" data-bind="text:lastModifiedForDisplay"></span> <span class="commands"> <a href="javascript:void(0)" data-bind="click:activate, visible: completed()"> activate </a> <a href="javascript:void(0)" data-bind="click:complete, visible: !completed()"> complete </a> <a href="javascript:void(0)" data-bind="click:remove">remove</a> </span> </div> </div> <div class="buttons"> <button data-bind="click: removeCompleted, enable:enableToRemoveCompleted"> remove completed </button> </div> </body> </html>
CSSも書きます
@charset "UTF-8"; body { padding:10px; color: #333; } button { padding: 3px 15px; } .todo-input-form { padding: 10px; border: 1px solid #ddd; } .todo-input-form .title-field { width: 200px; } .todo-input-form .error { color: #fa1188; } .todo-list { margin-left: 10px; } .todo { margin-top: 10px; } .todo span{ padding-right: 5px; } .todo .title { font-size: 110%; } .todo .last-modified { font-size: 80%; color: #999; } .todo .commands a { padding-right: 5px; } .buttons { margin-top: 10px; padding: 10px; border: 1px solid #ddd; }
最後はmain.js。
main.jsはhtmlで最初に読まれるスクリプトで、以下の処理を行います。
require.config({ baseUrl: "../js", paths: { "container" : "../../../../minified/container", "knockout" : "knockout-2.3.0" } }); require([ "container", "knockout", "composing/modules", "models/time-source", "models/todo-list", "models/todo", "viewmodels/todo-input-form", "viewmodels/todo-list-view", "viewmodels/todo-view" ], function( ContainerJS, ko, modules ) { var container = new ContainerJS.Container( modules ); container.get("todoListView").then(function( viewModel ){ ko.applyBindings(viewModel); }, function( error ) { alert( error.toString() ); }); });
必要なソースの作成はこれで完了。動いているところはこちらでみられます。
6.minify && 結合してリリース
最後に、ソースをminify && 結合してリリースするAntタスクを定義していきます。
- minify && 結合はRequire.jsからリリースされているr.jsを使用。
- Require.jsの依存関係をたどって必要なファイルを集め、1ファイルに統合します。
- closure等を使用してminifyを行う機能もあります。
- サンプルでは、main.jsにすべてのファイルを統合する形にしています。
- リリース版ではmain.jsが統合版に置き換わり、require.jsとmain.jsのみの読み込みとなります。
- 最初に読むファイルは変わらないので、HTMLの変更は不要。
Antタスクは以下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project name="todo lists" default="release" basedir="."> <property name="test.dir" value="test" /> <property name="tools.dir" value="../../tools" /> <property name="rhino.home" value="${tools.dir}/rhino1_7R4" /> <property name="jasmine.home" value="../../lib-test/jasmine-1.0.2" /> <property name="jasmine-reporters.home" value="../../lib-test/larrymyers-jasmine-reporters-adf6227" /> <property name="envjs.home" value="../../lib-test/thatcher-env-js-cb738b9" /> <property name="closure-compiler.home" value="${tools.dir}/compiler-20130603" /> .. 略 <target name="minify"> <java fork='true' dir="${basedir}" classname="org.mozilla.javascript.tools.shell.Main"> <classpath> <path path="${rhino.home}/js.jar" /> <path path="${closure-compiler.home}/compiler.jar" /> </classpath> <jvmarg line="-Xss1m"/> <arg line="-encoding utf-8 ${tools.dir}/r.js -o dist/build-config.json"/> </java> </target> </project>
build-config.jsonに minify && 結合 の設定を書きます。
({ appDir: "../src", baseUrl: "./js", paths: { "container" : "../../../../minified/container", "knockout" : "knockout-2.3.0" }, dir: "../dst", optimize: "closure", closure: { CompilerOptions: {}, CompilationLevel: 'SIMPLE_OPTIMIZATIONS', loggingLevel: 'WARNING' }, optimizeCss: "standard.keepLines", modules: [{ name: "main" }] })
タスクを実行すると
$ ant minify
「dst」ディレクトリ以下に最適化されたソースが出力されます。あとはこれをリリースすればOK。
リリース版はこちら。最適化前と比べてjsの読み込みが最小化されています。
JavaScriptアプリケーション用のDependency Injection コンテナ「ContaienrJS」の新版をリリース
夏休みの宿題ということで、作成してから長らくメンテナンスしていなかった ContaienrJS の新版をリリースしました。変更点は以下です。
- 新機能 : モジュールの非同期遅延読み込みに対応
- require.jsと連携し、コンポーネント(=コンテナ管理下のオブジェクト)が実際に必要とされるまで、そのJavaScriptソースの読み込みと評価を遅延します。
- ユーザーがボタンを押したらダイアログを表示するようなシーンで、ボタンが押されたタイミングでダイアログクラスをロードしてインスタンスを作成するといった制御が容易に実現できます。
- ↑これに伴い、
ダウンロード
ダウンロードは以下より。
unageanu / container-js - GitHub
ドキュメントはここにあります。DIコンテナとしての基本的な機能についてはこちらを参照ください。Aspectとかにも対応してます。
サンプル
具体的に動くものをいくつか。
samples/ 以下に完全なソースがあるのでそちらも参照ください。
Hello World
「Hello World」を出力するサンプルです。
ファイル構造:
├ index.html
└ scripts/
├ main.js
├ require.js
├ container.js
├ app/
│ ├ model.js
│ └ view.js
└ utils/
└ observable.jsscripts/app/model.js:
define(["utils/observable"], function(Observable){ "use strict"; /** * @class */ var Model = function() {}; Model.prototype = new Observable(); /** * @public */ Model.prototype.initialize = function() { this.fire( "updated", { property: "message", value :"hello world." }); }; return Model; });
scripts/app/view.js:
define(["container"], function( ContainerJS ){ "use strict"; /** * @class */ var View = function() { this.model = ContainerJS.Inject("app.Model"); }; /** * @public */ View.prototype.initialize = function() { this.model.addObserver("updated", function( ev ) { if ( ev.property != "message" ) return; var e = document.getElementById(this.elementId); e.innerHTML = ev.value; }.bind(this)); }; return View; });
scripts/app/main.js:
require.config({ baseUrl: "scripts", }); require(["container"], function( ContainerJS ) { var container = new ContainerJS.Container( function( binder ){ binder.bind("app.View").withProperties({ elementId : "console" }).onInitialize("initialize") .inScope(ContainerJS.Scope.EAGER_SINGLETON); binder.bind("app.Model"); }); window.addEventListener("load", function() { container.get("app.Model").then(function( model ){ model.initialize(); }, function( error ) { alert( error.toString() ); }); }, false); });
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Hello World</title> <script type="text/javascript" data-main="scripts/main.js" src="scripts/require.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="console"></div> </body> </html>
Lazy Loading
遅延読み込みのサンプルです。
リンクがクリックされたら、component.jsの読み込みとインスタンス化が行われます。
ファイル構造:
├ index.html
└ scripts/
├ main.js
├ require.js
├ container.js
└ app/
├ component.js
└ owner.jsscripts/app/component.js:
define(function(){ "use strict"; /** * @class */ var Component = function() { print("component : created."); }; return Component; });
scripts/app/owner.js:
define(["container"], function( ContainerJS ){ "use strict"; /** * @class */ var Owner = function() { this.component = ContainerJS.Inject.lazily("app.Component"); print("owner : created."); }; /** * @public */ Owner.prototype.initialize = function() { print( "owner : initialize." ); this.component.then(function( component){ }, function( error ) { alert( error.toString() ); }); }; return Owner; });
scripts/main.js:
require.config({ baseUrl: "scripts" }); require(["container"], function( ContainerJS ) { window.print = function( message ) { document.getElementById("console").innerHTML += message + "<br/>"; }; var container = new ContainerJS.Container( function( binder ){ binder.bind("app.Component"); binder.bind("app.Owner"); }); window.addEventListener("load", function() { container.get("app.Owner").then(function( owner ){ document.getElementById("link").addEventListener( "click", function(){ owner.initialize(); }); }, function( error ) { alert( error.toString() ); }); }, false); });
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Lazy Loading</title> <script type="text/javascript" data-main="scripts/main.js" src="scripts/require.js"></script> </head> <body> <div> <a id="link" href="javascript:void(0);">click.</a> </div> <div id="console"></div> </body> </html>
Method Interception
前からある機能ですが、コンポーネントのメソッドにインターセプタを差し込めます。
ファイル構造:
├ index.html
└ scripts/
├ main.js
├ require.js
├ container.js
└ app/
└ component.jsscripts/app/component.js:
define(function(){ "use strict"; /** * @class */ var Component = function() {}; Component.prototype.method1 = function( ) { print("method1 : executed."); }; Component.prototype.method2 = function( ) { print("method2 : executed."); }; return Component; });
scripts/main.js:
require.config({ baseUrl: "scripts" }); require(["container"], function( ContainerJS ) { window.print = function( message ) { document.getElementById("console").innerHTML += message + "<br/>"; }; var container = new ContainerJS.Container( function( binder ){ binder.bind("app.Component"); binder.bindInterceptor( function( jointpoint ) { print( "before : " + jointpoint.methodName ); var result = jointpoint.proceed(); print( "after : " + jointpoint.methodName ); return result; }, function(binding, component, methodName) { if (binding.name !== "app.Component" ) return false; return methodName === "method1" || methodName === "method2"; } ); }); window.addEventListener("load", function() { container.get("app.Component").then(function( component ){ document.getElementById("link1").addEventListener( "click", function(){ component.method1(); }); document.getElementById("link2").addEventListener( "click", function(){ component.method2(); }); }, function( error ) { alert( error.toString() ); }); }, false); });
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Method Interception</title> <script type="text/javascript" data-main="scripts/main.js" src="scripts/require.js"></script> </head> <body> <div> <a id="link1" href="javascript:void(0);">click to execute method1.</a>| <a id="link2" href="javascript:void(0);">click to execute method2.</a> </div> <div id="console"></div> </body> </html>
freeze/seal/preventExtensions の違いまとめ
ECMAScript 5 で追加された、Object.freezeやObject.sealを実行すると何ができなくなるのかについて。
こうなる。
| preventExtensions | seal | freeze | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| プロパティの追加 | × | × | × | |
| プロパティの削除 | ○ | × | × | |
| プロパティの値変更 | ○ | ○ | × | |
| プロパティの属性変更 | ○ | × | × |
確認。
(function() { //"use strict"; // strict モードにすると、Firefox,Google Chrome,SafariではflozenObjectへの属性の追加等でもTypeErrorが発生するようになる。 // IEでは、非strict モードと変わらない動作をする。 describe('Flozen Object', function() { var flozenObject; beforeEach(function() { defineMatcher(this); flozenObject = createObject(); Object.freeze( flozenObject ); }); it( 'should be fail to add property.', function() { flozenObject.x = "xxx"; expect(flozenObject.x).toBeUndefined(); }); it( 'should be fail to delete property.', function() { delete flozenObject.a; expect(flozenObject.a).toEqual("aaa"); }); it( 'should be fail to modify property.', function() { flozenObject.a = "xxx" ; expect(flozenObject.a).toEqual("aaa"); }); it( 'should be fail to configure property.', function() { expect( function(){ Object.defineProperty(flozenObject, "a", { enumerable : false }); }).toThrowTypeError(); }); }); describe('Sealed Object', function() { var sealedObject; beforeEach(function() { defineMatcher(this); sealedObject = createObject(); Object.seal( sealedObject ); }); it( 'should be fail to add property.', function() { sealedObject.x = "xxx"; expect(sealedObject.x).toBeUndefined(); }); it( 'should be fail to delete property.', function() { delete sealedObject.a; expect(sealedObject.a).toEqual("aaa"); }); it( 'should be success to modify property.', function() { sealedObject.a = "xxx" ; expect(sealedObject.a).toEqual("xxx"); }); it( 'should be fail to configure property.', function() { expect( function(){ Object.defineProperty(sealedObject, "a", { enumerable : false }); }).toThrowTypeError(); }); }); describe('Non Extensible Object', function() { var nonExtensibleObject beforeEach(function() { defineMatcher(this); nonExtensibleObject = createObject(); Object.preventExtensions( nonExtensibleObject ); }); it( 'should be fail to add property.', function() { nonExtensibleObject.x = "xxx"; expect(nonExtensibleObject.x).toBeUndefined(); }); it( 'should be success to delete property.', function() { delete nonExtensibleObject.a; expect(nonExtensibleObject.a).toBeUndefined(); }); it( 'should be success to modify property.', function() { nonExtensibleObject.a = "xxx" ; expect(nonExtensibleObject.a).toEqual("xxx"); }); it( 'should be success to configure property.', function() { expect( function(){ Object.defineProperty(nonExtensibleObject, "a", { enumerable : false }); }).toSuccess(); }); }); // utils function createObject() { return { a : "aaa" }; } function defineMatcher( spec ) { spec.addMatchers( { toSuccess : function(){ this.actual(); return true; }, toThrowTypeError : function(){ try { this.actual(); return false; } catch ( e ) { return e.name === "TypeError"; } } }); } }());
- strict モードにすると、Firefox,Google Chrome,SafariではfreezeされたObjectへの属性の追加等でもTypeErrorが発生するようになるので注意。
- 非strictモードでは、「実行はできるが何も効果がない」という動作となる。
- IE9では、モードに限らず同じ動作となる。
Closure CompilerでタイプセーフJavaScriptコーディング
Closure Compilerを使用したタイプセーフJavaScriptコーディングについてまとめ。
- Closure CompilerはClosure Toolsの一部で、
- JavaScriptコードを解析して圧縮と最適化を行うJavaScriptToJavaScriptコンパイラです。
- 最適化だけでなく、シンタックスや型のチェック機能も提供。
- 型チェックは、JsDocコメントの形式で記載された型情報をもとに行われます。
- 型システムは、ECMAScript4の仕様に準拠している模様。
- Closure Compilerを使用することで、ECMAScript3の世界でECMAScript4ライクな型システムが使えます。(型情報をコメントに書くので、スマートさには欠けますが・・)
Closure Compilerのインストール
- Closure Compilerのサイトよりzipアーカイブを取得して展開すればOK。
- Javaプログラムなので実行にはJREも必要です。インストールされていない場合は別途取得してインストールしておきます。
基本的な使い方
java -jar compiler.jar --charset <jsファイルのエンコード:デフォルトはUTF-8>
--compilation_level ADVANCED_OPTIMIZATIONS
--jscomp_error=checkTypes
--js <コンパイルするjaファイル>
--js_output_file <コンパイル結果を保存するファイル>
- デフォルトでは型チェック機能はoffになっているので、「--jscomp_error=checkTypes」を指定してチェックを有効化する必要があります。
- 「--compilation_level」は型チェック目的では何でもよいですが、せっかくなので最強の「ADVANCED_OPTIMIZATIONS」を使います。
- 「--charset」は、指定しなければファイルをUTF-8として扱うので、指定しなくてもいいっちゃいい。
具体例。以下のようなjsファイル(sample.js)を用意し、
/** * 数値を受け付ける関数。 * @function * @param {number} number */ function acceptNumber( number ){} acceptNumber( "a" ); // コンパイルエラー!
コンパイラを実行すると、
$ java -jar compiler.jar --compilation_level ADVANCED_OPTIMIZATIONS --jscomp_error=checkTypes --js sample.js --js_output_file compiled.js
sample.js:9: ERROR - actual parameter 1 of acceptNumber does not match formal parameter
found : string
required: number
acceptNumber( "a" ); // コンパイルエラー!
^
1 error(s), 0 warning(s), 100.0% typedという感じで、エラーが出力されます。
クラス/インターフェイス
基本となる、クラス/インターフェイスの定義の方法と使い方について。コンパイラは、オブジェクトに関連付けられたクラス/インターフェイスに基づいて、プロパティのチェックや互換性のチェックを行います。
クラスの定義
「@constructor」を付与したメソッドは、クラスを生成するためのコンストラクタメソッドとなり、メソッド名に対応するクラス(以下の例であれば"sample.ClassA")が定義されます。
var sample = {}; /** * クラスA * @constructor */ sample.ClassA = function () {};
- 「new」付きで呼び出す
- クラスのインスタンスを「this」として呼び出す
ことのみ可能です。2は派生クラスから親クラスのコンストラクタを呼び出すときに使います。
new sample.ClassA(); // new 付きで呼び出すことは可能。 sample.ClassA.call( new sample.ClassA() ); // sample.ClassAのインスタンスをthisとして実行するのもOK sample.ClassA(); // コンパイルエラー! sample.ClassA.call( "a" ); // コンパイルエラー!
フィールド/メソッドの定義
フィールドやメソッドの定義は以下のとおり。
- フィールドの型は「@type {<型>}」で指定します。
- メソッドの引数は「@param {<型>} <引数名>」、戻り値は「@return {<型>}」で指定します。
/** * クラスA * @constructor */ sample.ClassA = function () { /** * クラスAのフィールド * @type {number} */ this.propertyA = 5; }; /** * クラスAのメソッド * @function * @param {number} arg1 引数1 * @return {string} 戻り値 */ sample.ClassA.prototype.methodA = function(arg1){ return "methodA"; }; /** * クラスAのフィールド2 * @type {number} */ sample.ClassA.prototype.propertyB;
クラスを使ってみます。
/** @type {sample.ClassA} */ // ローカル変数の型も@typeで明示します。 var a = new sample.ClassA(); a.propertyA = 10; a.propertyB = "a"; // コンパイルエラー! : 型が不一致 var n = a.propertyUndefined; // これはOK a.propertyUndefined = "a"; // これはOK a.methodA(10); a.methodA("a"); // コンパイルエラー! : 型が不一致 a.methodUndefined(10); // コンパイルエラー! : 未定義のメソッド
- クラスで定義されていないメソッドを呼び出したり、引数の型があわない場合コンパイルエラーとなります。
- フィールドの型があわない場合もコンパイルエラーとなります。
- 未定義フィールドへの代入や参照は可能とされているみたい。
delete a.propertyA; delete a.propertyB; delete a.methodA;
継承
「@extends {<親クラス>}」を付与すると、派生クラスとなります。
注意:「型システム上で派生クラスとみなされる」だけで、JavaScriptでの継承操作(「sample.ClassA2.ptototype = new sample.ClassA();」のような操作)は別途必要です。
/** * クラスAの派生クラス * @constructor * @extends {sample.ClassA} */ sample.ClassA2 = function () { sample.ClassA.call(this); // 親クラスのコンストラクタを呼び出す。 }; // JavaScriptでの継承操作は別途必要。 // ↓はClosure Libraryの機能を使って継承を実現する例。 goog.inherits(sample.ClassA2, sample.ClassA);
派生クラスなので、親クラスのメソッドやフィールドが使えるとみなされます。また、親クラス型の変数に代入できます。
/** @type {sample.ClassA2} */ var a2 = new sample.ClassA2(); // 親クラスのメソッド、フィールドにアクセスできる。 a2.propertyA = 10; a2.methodA(10); /** * クラスAと継承関係のないクラスB * @constructor */ sample.ClassB = function () {}; // 変数への代入 // ClassA型の変数には、ClassAおよびその派生クラスを代入できる。 /** @type {sample.ClassA} */ var classA = new sample.ClassA(); /** @type {sample.ClassA} */ var classA2 = new sample.ClassA2(); /** @type {sample.ClassA} */ var classB = new sample.ClassB(); // コンパイルエラー!
多重継承は不可です。
/** * クラスA,クラスBを多重継承 * @constructor * @extends {sample.ClassA} * @extends {sample.ClassB} // これはコンパイルエラー。 */ sample.ClassX = function () {};
インターフェイス
インターフェイスも作れます。「@interface」を付与すればOK。
var sample = {}; /** * インターフェイスA * @interface */ sample.InterfaceA; /** * インターフェイスのメソッド。 * 実装クラスが実装する必要がある。 * @function * @param {number} arg1 */ sample.InterfaceA.prototype.methodA; /** * インターフェイスの属性。 * これも実装クラスで実装する必要がある。 * @type {number} */ sample.InterfaceA.prototype.propertyA; /** * インターフェイスB * @interface */ sample.InterfaceB = function(){}; /** * @function * @param {number} arg1 */ sample.InterfaceB.prototype.methodB;
インターフェイスを実装するには、実装先のクラスに「@implements {<インターフェイス名>}」を付与します。
/** * インターフェイスA,Bを実装したクラス。 * @constructor * @implements {sample.InterfaceA} * @implements {sample.InterfaceB} // 複数のインターフェイスを実装できる。 */ sample.InterfaceAAndBImplemented = function(){ /** @override */ this.propertyA = "a"; }; /** @override */ sample.InterfaceAAndBImplemented.prototype.methodA = function(arg1){alert(arg1+"a");}; /** @override */ sample.InterfaceAAndBImplemented.prototype.methodB = function(arg1){alert(arg1+"b");};
使ってみます。
/** @type {sample.InterfaceA} */ var interfaceA = new sample.InterfaceAAndBImplemented(); // 実装クラスのインスタンスはインターフェイス型の変数に代入可能。 /** @type {sample.InterfaceB} */ var interfaceB = new sample.InterfaceAAndBImplemented(); interfaceA.propertyA = 10; interfaceA.propertyA = "x"; // コンパイルエラー! interfaceA.methodA(1); interfaceB.methodB(1); interfaceA.methodC("x"); // コンパイルエラー!
実装クラスで必要なメソッドや属性が実装されていない場合、コンパイルエラーとなります。
/** * sample.InterfaceA の実装クラス2。 * インターフェイスのメソッドが実装されていないため、コンパイルエラーになる。 * @constructor * @implements {sample.InterfaceA} */ sample.InterfaceAImplemented2 = function(){};
型の種類
型として指定できる値には、↑のようなユーザー定義クラス/インターフェイスのほか、number,stringといった「Value Type」や、組み込みのArray、Objectなどいくつか種類があります。
型の種類一覧
- * (All Type)
- number
- string
- boolean
- null
- undefined
- Object
- Array
- 関数型 (Function Type)
- レコード型 (Record Type)
- String,Number,Dateなどのビルトインクラス
- ユーザー定義クラス
Value Type
ECMAScriptのプリミティブ値 (Primitive Value)に対応する型で、
- number
- string
- boolean
- null
- undefined
があります。
- Value Type は Objectのサブタイプではなく、null以外のオブジェクトはObject型変数と代入互換性がありません。
- 別の型として「Number」「String」「Boolean」があり、こちらはECMAScriptにおける「Stringオブジェクト」や「Numberオブジェクト」に対応します。
- Value Typeと違ってObjectのサブタイプなので、Object型変数に代入できます。
- Value Typeとの互換性はありません。
/** * プリミティブの数値型変数 * @type {number} */ var primitiveNumberType; /** @type {number} */ var primitiveNumberVar = primitiveNumberType; /** @type {Number} */ var numberVar = primitiveNumberType; // コンパイルエラー! /** @type {Object} */ var objectVar = primitiveNumberType; // コンパイルエラー! primitiveNumberType = 1; primitiveNumberType = new Number(1); // コンパイルエラー! primitiveNumberType = null; // コンパイルエラー! /** * 数値オブジェクト型変数 * @type {Number} */ var numberType; /** @type {number} */ var primitiveNumberVar2 = numberType; // コンパイルエラー! /** @type {Number} */ var numberVar2 = numberType; /** @type {Object} */ var objectVar2 = numberType; numberType = 1; // コンパイルエラー! numberType = new Number(1); numberType = null;
Object Type
「Object」とその派生型。
- サブタイプとしてArray、Dateといった組み込みの型があります。
- ユーザー定義クラスもObject派生となります。
/**@type {Object}*/ var objectType; /**@type {Array}*/ var arrayType; /**@type {Date}*/ var dateType; objectType = {}; objectType = []; objectType = new Date(); arrayType = {}; // コンパイルエラー! arrayType = []; arrayType = new Date(); // コンパイルエラー! dateType = {}; // コンパイルエラー! dateType = []; // コンパイルエラー! dateType = new Date();
Function Type
関数を示す型です。
- 「{function(<パラメータの型...>):<戻り値の型>}」の形式で記述します。
- 結果を返さない関数の場合、戻り値型はvoidとします。
- Object派生です。
/** * 関数型の変数。 * {function(<パラメータの型...>):<戻り値の型>}の形式で指定する。 * * @type {function(string,number):string} */ var function1 = function( arg1, arg2 ) { return "aaa"; }; function1("a", 1); function1("a", "a"); // コンパイルエラー! : 第2引数の型が不一致 function1("a", 1, "a"); // コンパイルエラー! : 引数の数が不一致 /**@type {number}*/var var1 = function1("a", 1); // コンパイルエラー! : 戻り値の型が不一致 /** * 結果を返さない関数の場合、戻り値型はvoidとする。 * * @type {function(string,number):void} */ var function2 = function( arg1, arg2 ) { }; /**@type {number}*/var var2 = function2("a", 1); // コンパイルエラー!
Object派生なので、Object型変数に代入できます。また、関数型同士も以下の条件を満たしている場合サブタイプとみなされ、代入互換性を持ちます。
- 関数型AとBがあり、以下の条件を満たす場合、関数型Aは関数型Bのサブタイプとなる。
- Aの引数の型が、Bと同じかスーパータイプである。
- Aの戻り値型が、Bと同じかサブタイプである。
// 関数型の互換性確認 /** @type {function(Object):Object} */ var acceptObjectRetunObject; /** @type {function(Date):Object} */ var acceptDateRetunObject; /** @type {function(Object):Date} */ var acceptObjectRetunDate; // 以下の条件を満たす場合、サブタイプとみなされ代入互換性を持つ。 // - 引数の型が同じかスーパータイプである。 // - 戻り値が同じかサブタイプである。 /** @type {function(Object):Object} */ var acceptObjectRetunObject2 = acceptDateRetunObject; // コンパイルエラー! : 引数の互換性がない /** @type {function(Object):Object} */ var acceptObjectRetunObject3 = acceptObjectRetunDate; /** @type {function(Date):Object} */ var acceptDateRetunObject2 = acceptObjectRetunObject; /** @type {function(Date):Object} */ var acceptDateRetunObject3 = acceptObjectRetunDate; /** @type {function(Object):Date} */ var acceptObjectRetunDate2 = acceptObjectRetunObject; // コンパイルエラー! : 戻り値の互換性がない /** @type {function(Object):Date} */ var acceptObjectRetunDate3 = acceptDateRetunObject; // コンパイルエラー! : 戻り値,引数共に互換性がない
ECMAScript4のオーバービューでは、引数の数も同じでないとダメとなっていますが、Closure Compilerでは互換性があれば違っていてもOKのようです。
// 引数の数は違っていてもOK /** @type {function(string):string} */ var acceptString; /** @type {function(string,number):string} */ var acceptStringAndNumber; /** @type {function(string):string} */ var acceptString2 = acceptStringAndNumber; /** @type {function(string,number):string} */ var acceptStringAndNumber2 = acceptString;
All Type
All Typeはすべての型のスーパータイプです。
- 型として、「{*}」を指定すると、All Typeになります。
- すべての型のスーパータイプなので、All Type型の変数にはすべての値を代入できます。
- 定義されているかどうか不明なメソッドを呼び出してもコンパイルエラーにはなりません。
- この挙動はどうなんだろう・・・。すべての型のUnion(後述)的な扱いなのかな・・・。
/** * 任意の値を代入可能な変数。 * @type {*} */ var allType; // すべての型の親クラス扱いなので、stringやObject型の変数に代入できない。 /** @type {string} */ var stringVar = allType; // コンパイルエラー! /** @type {number} */ var numberVar = allType; // コンパイルエラー! /** @type {Object} */ var objectVar = allType; // コンパイルエラー! // 定義されているかどうか不明なメソッドを呼び出してもコンパイルエラーにはならない。 allType.foo(); allType.foo2(); // あらゆる値を代入可能。 allType = "a"; allType = 1; allType = []; allType = function(){}; allType = false; allType = undefined; allType = null;
ECMAScript4のオーバービューでは、"Any"になってますね。
Record Type
「規定されたプロパティ一式を持つオブジェクト」を示す型です。
- 「{<プロパティ名>:<型>,....}」の形式で記述します。
- オブジェクトが、指定された型と名前のプロパティをすべて持つ場合、この型にマッチします。
/** * 文字列型のプロパティaと関数型のプロパティbを持つオブジェクトを格納可能な変数。 * @type {{a:string,b:function():string}} */ var hasAAndB; hasAAndB = {a:"aaa", b:function(){return "b";}}; hasAAndB = {a:"aaa"}; // コンパイルエラー! : プロパティbがない hasAAndB = {a:"aaa", b:5}; // コンパイルエラー! : プロパティbの型が不一致 hasAAndB = {a:"aaa", b:function(){return "b";}, c:5}; // 属性が多いのはOK hasAAndB.a = "a"; hasAAndB.b(); hasAAndB.x(); // コンパイルエラー! hasAAndB.x = "x"; // これはOK delete hasAAndB.x; // これもOK
レコード型は、
- 「互換性があり、かつ、より制約条件の緩い」レコード型のサブタイプとなります。
- 上記条件を満たしていれば、クラスのインスタンスもサブタイプと判定されます。
- ECMAScript4にあるlike演算子とかはつけなくてもよいみたい。
// 代入互換の確認 // 制限が緩くなり、型安全でなくなるパターンはコンパイルエラーとなる。 /** @type {{x:string,y:number}} */ var hasXAndY; /** @type {{x:string}} */ var hasX; /** @type {{y:number}} */ var hasY; /** @type {{x:string,y:number}} */ var hasXAndY2 = hasX; // コンパイルエラー! /** @type {{x:string,y:number}} */ var hasXAndY3 = hasY; // コンパイルエラー! /** @type {{x:string}} */ var hasX2 = hasXAndY; /** @type {{x:string}} */ var hasX3 = hasY; // コンパイルエラー! /** @type {{y:number}} */ var hasY2 = hasXAndY; /** @type {{y:number}} */ var hasY3 = hasX; // コンパイルエラー! // クラスも互換性があれば型にマッチする。 var sample = {}; /** @constructor */ sample.ClassA = function(){ /** @type {string} */ this.x = ""; } /** @constructor */ sample.ClassB = function(){} /** @constructor */ sample.ClassC = function(){ /** @type {number} */ this.x = 1; } hasX = new sample.ClassA(); hasX = new sample.ClassB(); // コンパイルエラー! : プロパティがない hasX = new sample.ClassC(); // コンパイルエラー! : プロパティはあるが型が不一致
型の結合
Union Typeとして、「任意の型のいずれか」を示す型を記述できます。
- 「{(<型1>|<型2>)}」の形式で、結合する型を「|」区切りで並べればOK。
- ECMAScript4のものとは微妙に記法が違います。
/** * boolean または number を代入可能な変数 * @type {(boolean|number)} */ var booleanOrNumber; booleanOrNumber = false; booleanOrNumber = 1; booleanOrNumber = "a"; // コンパイルエラー!
Union Typeは、「結合した型すべてと同じかまたはスーパータイプ」となる型のサブタイプとなります。具体的には以下のサブタイプとなります。
- 結合した型またはそのスーパータイプをすべてを含む別のUnion Type
- 結合した型すべてに共通する親クラス
// 以下の派生関係にあるクラスを作る。 // ClassA // + ClassB // + ClassC // ClassX /** @constructor */ sample.ClassA = function(){} /** @function */ sample.ClassA.prototype.methodA = function(){alert("a");}; /** @type {string} */ sample.ClassA.prototype.propertyA = "aa"; /** * @constructor * @extends {sample.ClassA} */ sample.ClassB = function(){} /** @function */ sample.ClassB.prototype.methodB = function(){alert("b");}; /** @type {string} */ sample.ClassB.prototype.propertyB = "bb"; /** * @constructor * @extends {sample.ClassA} */ sample.ClassC = function(){} /** @function */ sample.ClassC.prototype.methodC = function(){alert("c");}; /** @type {string} */ sample.ClassC.prototype.propertyC = "bb"; /** @constructor */ sample.ClassX = function(){} /** @function */ sample.ClassX.prototype.methodX = function(){alert("x");}; /** * sample.ClassB または sample.ClassC を代入可能な変数 * @type {(sample.ClassB|sample.ClassC)} */ var BorC; //結合した要素またはスーパータイプをすべて持つ別のUnion Typeのサブタイプとなる。 /** @type {(sample.ClassB|sample.ClassC|sample.ClassX)}*/ var BorCorX = BorC; /** @type {(sample.ClassA|sample.ClassX)}*/ var AorX = BorC; // sample.ClassA はsample.ClassB,sample.ClassC両方のスーパータイプなのでOK /** @type {(sample.ClassC|sample.ClassX)}*/ var CorX = BorC; // コンパイルエラー! // 結合した要素の共通の親のサブタイプとなる。 /** @type {sample.ClassB}*/ var b = BorC; // コンパイルエラー! /** @type {sample.ClassC}*/ var c = BorC; // コンパイルエラー! /** @type {sample.ClassA}*/ var a = BorC; /** @type {Object}*/ var o = BorC; /** @type {sample.ClassX}*/ var x = BorC; // コンパイルエラー!
メソッドやフィールドの扱いはどうなるかというと、現状では特にチェックされていないようです・・。仕様なのか未実装なのか、それともバグなのかは不明。
/** * sample.ClassB または sample.ClassC を代入可能な変数 * @type {(sample.ClassB|sample.ClassC)} */ var BorC; // メソッド/フィールドのチェックは行われていない模様。 // 仕様なのか未実装なのか、それともバグなのかは不明・・・。 BorC.methodA(); BorC.methodB(); // コンパイルエラーになるかも、と思ったがエラーにはならず。 BorC.methodC(); // コンパイルエラーになるかも、と思ったがエラーにはならず。 BorC.methodX(); // ClassB,ClassCのどちらでも定義されておらず明らかに不正だが、コンパイルエラーになったりはしない・・・。 BorC.propertyA = 1; BorC.propertyB = 1; // コンパイルエラーになったりはしない・・・。 BorC.propertyX = 1; // コンパイルエラーになったりはしない・・・。
型パラメータ
型パラメータを使って、配列の要素やObjectのキーと値の型を制限できます。
- ECMAScript4では、型パラメータを受け付けるクラスやインターフェイスが作れるようだけど、
- Closure Compilerのドキュメントでは説明なし・・・。現状では、配列とObjectでのみ使えるようです。
var sample = {}; /** * @constructor */ sample.ClassA = function(){}; // 配列の要素の型を指定 /** @type {Array.<string>} */ var stringArray = []; /** @type {Array.<number>} */ var numberArray = []; /** @type {Array.<sample.ClassA>} */ var objectArray = []; stringArray[0] = ""; stringArray[1] = 1; // コンパイルエラー! stringArray[2] = new sample.ClassA(); // コンパイルエラー! numberArray[0] = ""; // コンパイルエラー! numberArray[1] = 1; numberArray[2] = new sample.ClassA(); // コンパイルエラー! objectArray[0] = ""; // コンパイルエラー! objectArray[1] = 1; // コンパイルエラー! objectArray[2] = new sample.ClassA(); /** @type {string} */ var string = stringArray[0]; /** @type {number} */ var number = stringArray[0]; // コンパイルエラー // Objectのキーと値の型を指定する。 /** @type {Object.<string, string>} */ var stringMap = {}; stringMap["a"] = "a"; stringMap[1] = "b"; // コンパイルエラー! stringMap["b"] = 1; // コンパイルエラー! /** @type {string} */ var stringVar = stringMap[""]; /** @type {number} */ var numberVar = stringMap[""]; // コンパイルエラー!
型パラメータ付きオブジェクトの代入互換性
試してみた限り、特にチェックはされていない感じですねー。いいのかな。
/** * ClassAの派生クラス * @constructor * @extends {sample.ClassA} */ sample.ClassB = function(){}; /** * ClassAと継承関係のないクラス * @constructor */ sample.ClassC = function(){}; //スーパータイプやサブタイプを要素に持つ配列に代入してもエラーにならず・・・。 /** @type {Array.<Object>} */ var parentArray = objectArray; /** @type {Array.<sample.ClassB>} */ var subtypeArray = objectArray; /** @type {Array.<sample.ClassC>} */ var othertypeArray = objectArray; /** * ClassAを要素に持つ配列を受け付けるメソッド * @param {Array.<sample.ClassA>} arg1 */ function acceptArrayOfClassA(arg1) {alert(arg1.length);}; // スーパータイプやサブタイプを要素に持つ配列を渡してもエラーにならず・・・。 acceptArrayOfClassA(parentArray); acceptArrayOfClassA(subtypeArray); acceptArrayOfClassA(othertypeArray);
型パラメータの制約やvariance annotationとかもなし。これらはECMAScript4でも用意されていませんね。
Nullable
型の前に「!」または「?」を付与することで、「値をnullにできるかどうか」を指定できます。
- 「!」を付与すると、null不可、
- 「?」を付与すると、null可( {(<型>|null)}と同じ扱い )になります。
- 明示しない場合のデフォルト動作は以下のとおりです。
- 関数型、string、number、booleanはnull不可
- その他はnull可
/** * プリミティブの数値型変数 * @type {number} */ var primitiveNumberType; /** * null可のプリミティブの数値型変数 * @type {?number} */ var nullablePrimitiveNumberType; /** * null不可のプリミティブの数値型変数 * @type {!number} */ var nonNullablePrimitiveNumberType; primitiveNumberType = 1; primitiveNumberType = null; // コンパイルエラー! nullablePrimitiveNumberType = 1; nullablePrimitiveNumberType = null; nonNullablePrimitiveNumberType = 1; nonNullablePrimitiveNumberType = null; // コンパイルエラー! // 指定しない場合の、デフォルト動作の確認。 // 関数型、string、number、booleanはnull不可となる。 /** * @type {string} */ var stringType; /** * @type {function():void} */ var functionType; /** * @type {Object} */ var objectType; functionType = null; // コンパイルエラー! stringType = null; // コンパイルエラー! objectType = null;
特殊な引数
引数の型として指定できる特殊な記法について。関数型の引数部分、またはクラスやインターフェイスメソッドの@paramの型部分で使えます。
可変長引数
「...[<型>]」で可変長の引数を指定できます。
/** * 可変長引数を受け付ける関数 * @type {function(...[string]):string} */ var acceptVarArgs = function() { return "aaa"; }; acceptVarArgs("a"); acceptVarArgs("a", "b", "c"); acceptVarArgs(); // 引数なしもOK acceptVarArgs("a", 1, "b"); // コンパイルエラー! // @paramタグで使用する場合、[]は不要。 var sample = {}; /** * @constructor */ sample.ClassA = function(){}; /** * @function * @param {...string} args 可変長引数 */ sample.ClassA.prototype.acceptVarArgs = function(args){}; /**@type {sample.ClassA}*/ var a = new sample.ClassA(); a.acceptVarArgs("a"); a.acceptVarArgs("a","b","c"); a.acceptVarArgs(); a.acceptVarArgs("a", 1, "b"); // コンパイルエラー!
指定してもしなくてもよい引数
型の後に「=」を付与すると、指定してもしなくてもよい引数となります。
/** * 指定してもしなくてもよい引数を受け付ける関数 * @type {function(string,number=):string} */ var acceptOptionalArg = function() { return "aaa"; }; acceptOptionalArg("a", 1); acceptOptionalArg("a"); acceptOptionalArg("a", "b");// コンパイルエラー! acceptOptionalArg("a", null);// コンパイルエラー! var sample = {}; /** * @constructor */ sample.ClassA = function(){}; /** * @function * @param {string} arg1 * @param {number=} arg2 指定してもしなくてもよい引数。 */ sample.ClassA.prototype.acceptOptionalArg = function(arg1,arg2){}; /**@type {sample.ClassA}*/ var a = new sample.ClassA(); a.acceptOptionalArg("a", 1); a.acceptOptionalArg("a"); a.acceptOptionalArg("a", "b");// コンパイルエラー! a.acceptOptionalArg("a", null);// コンパイルエラー!
型定義
「@typedef」を使って、型を定義できます。
var sample = {}; // 型を定義 /** * @typedef {{each:function(*):void}} */ sample.Enumerable; // 定義した型を使うメソッド /** * map関数 * @param {sample.Enumerable} enumerable * @return {Array.<*>} */ function map( enumerable ) { var result = []; enumerable.each( function(item){ result.push(item); }); return item; } var array = map({ each : function( f ) { for ( var i=0;i<10;i++) f(i); } }); // 以下はコンパイルエラー! : sample.Enumerable型にマッチするeachがない map({ each : "" });
Record TypeやUnion Typeを再利用する場合に使う機能みたいですね。
インターフェイスやクラスを使う手もありますが、必要なメソッド数が少ない場合はこちらのほうがシンプルに書けそうかな。
型推論
ちゃんとしたキュメントが見つけられなかったのであれですが、サンプルコードを書いて試していると「これ型推論してるんじゃね?」と思わせる挙動がいくつかあったので紹介。
// 変数の型が明示されていなくても、代入された値から型を推論してチェックする。 var array = ["a","b"]; array.join("x"); var n = array.length; array.undefinedMethod(); // コンパイルエラー。 // 変数の型が明示されていても、代入された値があればその型に応じてチェックが行われる。 /** @type {Object} */ var object = new Date(); object.getTime(); object.undefinedMethod(); // コンパイルエラー。 object = ["a","b"]; object.join("x"); n = object.length; object.undefinedMethod(); // コンパイルエラー。 // 関数の戻り値から推論 /** * @function * @return {Date} */ function now() { return new Date(); }; var d = now(); d.getTime(); d.undefinedMethod(); // コンパイルエラー。
感想など
JavaScriptコードも規模がそこそこ大きくなってくると静的な型チェック機能が欲しくなってきますよね?
- numberのはずのIDがいつの間にかstringになっていてエラー
- ライブラリAPIに渡す引数の順番を間違えていてエラー
といった不毛なバグを回避したいなら、利用を検討してみてはどうでしょうか?特に中規模以上プロジェクトで複数人で開発するような場合、効果はあるかと思います。タイプセーフコーディング以外にも「型情報を使用したJavaScriptコードの最適化」とかも期待できるかもです。(このへんはぜんぜん見れていませんが・・・)
利用にあたって問題になりそうなことは、使用するライブラリの対応ですかね。ライブラリに型情報が記載されていないと機能しないので、JsDocがちゃんと書かれていないライブラリだとまったく使えない・・・。実質的にClosure Libraryを使うことになるのですが、絶賛開発中な感じなのがちょっと・・・。Collectionクラスは妙に充実していますが。あとは、prototype.jsやdojoにあるようなクラス定義ユーティリティとの相性も気になるところです。
IE7のメモリリーク問題
IE7には、以下の条件を満たす場合メモリリークが発生する問題があります。
- DOMエレメントとJSオブジェクトが循環参照している
- 上記エレメントをスクリプトで削除する
IE8では改修されているようでこの問題は発生しません。また、Firefox 3でも発生しません。
循環参照とメモリリークの例
function test1() { // DOMエレメントとJSオブジェクトの循環参照の例。 // IE6ではこれだけでリークが発生したらしいが、IE7以降では発生しない。 var largeData = createLargeData(); var div = document.getElementById("div"); // DOMエレメント div.foo = function() {}; // JSオブジェクト // closureにより、このオブジェクトはdiv,largeDataの参照を保持する。 // →JSオブジェクトとDOMエレメントの循環参照が発生。 } function test2() { // IE7でリークが発生するパターン。複数回実行するとリークが発生する。 // 以下のように循環参照したエレメントがスクリプトで破棄され、アンロード時に存在しないとGCの対象にならない。 var largeData = createLargeData(); document.getElementById("div").innerHTML = "<div id='created'>created</div>"; // 循環参照したままドキュメントから削除。 var created = document.getElementById("created"); created.foo = function() {}; // IE8ではこの問題は改修されており発生しない。Firefoxでも発生しない。 }
確認はこちら。IE7でtest2のリンクをクリックしていると、使用メモリががしがし増えていきます。IE8,Firefoxでは問題なし。
対策
で、対策ですが、「削除する前に循環参照を切る」とか「そもそも循環参照させない」とかでOK。
function fix1() { // リークを回避するためには、削除の前に参照を切ってやればOK。 var largeData = createLargeData(); var created = document.getElementById("created"); if (created) delete created.foo; // 循環参照を切る。 document.getElementById("div").innerHTML = "<div id='created'>created</div>"; var created = document.getElementById("created"); created.foo = function() {}; } function fix2() { // そもそも循環参照させない。 (function(){ var largeData = createLargeData(); document.getElementById("div").innerHTML = "<div id='created'>created</div>"; return document.getElementById("created"); })().foo = function() {}; }
XMLHttpRequestの最大同時接続数
AJAXサイトの定期観測向け性能計測ツールを作ってみた
AJAXサイトの定期観測向け性能計測ツールを作ってみましたよ。
- ページの読み込み時間、サーバーAPIの呼び出し時間ならJMeter、JavaScriptの実行時間ならBenchmark.jsで計測できるけど、
- これらをひっくるめた読み込みを開始してから画面に情報が表示されるまでにかかる一連の時間を計測するツールとなるとFireBugくらいしか見当らないなー・・・。
- FireBugでも計測はできるけど、計測対象ページがいっぱいあったり、5回計測して平均をとる、とかいう場合にはちょいシンドイ。
- FireBug自体のオーバーヘッドも若干気になるし・・。
- あと、IE7,8でも測らんといかんので、同じ仕組みでIEでもFireFoxでも計測できるようにしておきたい。
というのが経緯。「ログ出力監視方式」の計測ツールならこれらの要件を満たせそう && 割とさくっと作れそうじゃね?と思い立って作ってみました。
仕組みと機能
- 計測対象のサイトをインラインフレーム内に読み込んで、あらかじめ仕込んでおいたログが出力されるまでの時間を計測するという仕組みです。
- ○ページの読み込み時間から、サーバーAPIの呼び出し時間、JavaScriptの実行時間を含めた読み込みを開始してから画面に情報が表示されるまでにかかる一連の時間を計測できます。
- ○特定のブラウザに依存しません。IE、Firefoxそれぞれの計測を同じツールで行えます。(原理的には)
- ×計測対象ページにあらかじめログ出力コードを埋めておく必要があります。
- ×iframeへのロードが禁止されていると計測できません。
- 計測対象のページや計測内容は、JavaScripで定義する方式です。
- 複数のテストを定義しておいて、まとめて実行できます。
- 指定された回数実行して平均、最大、最小を表示する機能もご用意。
-
- まぁ、必要ですよね。
-
プロファイラ的な使い方も無理すればできますが、それはFireBugやIEのデバッグツールを使ったほうが便利。
- そこそこページの多いサイトを作っていて、
- 各ページの表示性能を定期的に一括計測できるようにしておきたい!
という場合向きです。
ダウンロード
ファイル数が若干多いので、Google Codeに置いてます。
→perfjs - Download
使い方
概要は以下。
1.プロジェクトに計測ツール一式を取り込む
ダウンロードしたzipに含まれるフィルのうち、以下をプロジェクトに取り込みます。
- html/**
- css/**
- lib/**
配置場所は、HTTPで公開される場所であればどこでもOKです。
2.計測対象ページにログを埋め込む。
次に、計測対象とするページにログを埋め込みます。
- lib/perf-logger.jsにロガーの実装があるので、計測対象ページでこれを読み込んで、
- 「perf.logger.executed("<イベントID>");」を計測ポイントに入れていきます。
// ログを出力。 perf.logger.executed("test"); // "test-<NO>"を記録。 // <NO>はイベントの識別用番号で、イベントごとに1から順に採番されます。 // 一定の期間を計測するユーティリティもあります。 var end = perf.logger.start("test"); // "start-test-<NO>"を記録。 setTimeout( function() { end(); // "end-test-<NO>"を記録 }, 1000);
「perf.logger.*」はデフォルトでは何も実行しない空関数なので、実行しても何も起こりません。ページがiframeに読み込まれた際に、ツールによって上書きされます。
3.テストスクリプトを書く
ログを仕込んだら、次にテストスクリプトを用意します。「samples/script.js」にサンプルがあるので参考に。
// テスト定義 // 「../samples/test1.html」 を読み込んでdocument.onloadが呼ばれるまでの時間を計測する簡単なもの。 perf.regist({ // テストの識別用ID id : "test1", // 計測対象とする一連の処理。これの開始と終了までの所要時間が計測されます。 test: [ // 「../samples/test1.html」を読み込む。 perf.ops.load( "../samples/test1.html" ), // 「loaded-1」が出力されるまで待機する。 // 「loaded」イベントは出力コードを書かなくても、document.onloadのタイミンクで自動で記録されます。 perf.ops.wait( perf.exps.logged( "loaded-1" )) ] }); // 「../samples/test3.html」を読み込んで、ページで定義されているグローバル関数「log」を実行し、処理が完了するまでを計測するサンプル。 perf.regist({ id : "test3. サイトの関数を実行", // 前準備として実行する一連の処理。 // testと違ってこちらの所要時間は計測範囲に含まれません。 // また、後始末としてteardownも定義できます。 setup: [ perf.ops.load( "../samples/test3.html" ), // 「../samples/test3.html」を読み込み perf.ops.wait( perf.exps.logged( "loaded-1" )) // 読み込み完了を待つ ], test: [ // 「../samples/test3.html」のグローバル関数「log」x3を実行。 perf.ops.call( function( global ) { global.log( "a" ); setTimeout( function(){ global.log( "b" ); }, 200); setTimeout( function(){ global.log( "c" ); }, 500); }), // グローバル関数「log」の処理完了を示すログがすべて出力されるのを待機する。 perf.ops.wait( perf.exps.all( perf.exps.logged( "end-a-1" ), perf.exps.logged( "end-b-1" ), perf.exps.logged( "end-c-1" ) )) ] });
作成が完了したら、「./html/index.html」でスクリプトをロードする設定を行ってください。
... (略) <script type="text/javascript" src="../samples/scripts.js"></script>
4. index.html にアクセス。
あとは、アプリケーションサーバーなりWebサーバーなりを起動して、「./html/index.html」にアクセスすればOK。
・・・
やや突貫工事だったりするのでUIとかいろいろショボイですが・・・。とりあえずこれでストップウォッチは回避できるかな。