[Ruby]ダイクストラ アルゴリズムでグラフデータ中の2点間の最短経路を算出する
ダイクストラ アルゴリズム で、グラフデータ中の2点間の最短経路を算出してみます。
まずは、グラフのデータ構造を作成。とりあえずグラフの構築と探索に必要な最低限のAPIのみ用意しました。
- Graph
- グラフです。
- verticesフィールド でグラフ中の頂点を配列で持ちます。
- Graph#add_vertexで頂点を追加できます。
- 各頂点には、追加時にIDが割り振られます。
- Graph#connect,disconnectでグラフ中の頂点同士を接続できます。
- 接続時には「重み」が指定でき、より軽い経路が最短とされます。
- Vertex
- 頂点です。Graph#verticesで保持されるオブジェクトです。
- edgesフィールドで経路(接続されている頂点と経路の重みのペア)の配列を持ちます。
# グラフ class Graph def initialize( directed=false ) @serial = 0 @directed = directed @vertices = [] end def connect( from, to, weight=1 ) assert_vertex_exist from assert_vertex_exist to @vertices[from].connect( to, weight ) @vertices[to].connect( from, weight ) unless @directed end def disconnect( from, to ) assert_vertex_exist from assert_vertex_exist to @vertices[from].disconnect( to ) @vertices[to].disconnect( from, weight ) unless @directed end def add_vertex( data ) id = @serial @serial += 1 @vertices[id] = Vertex.new( id, data ) return id end def inspect return "---\n" + vertices.collect {|v| v.inspect }.join("\n") end attr_reader :vertices private def assert_vertex_exist( id ) if ( id < 0 || id >= @vertices.length || !@vertices[id] ) raise "vertex not exist. id=#{id}" end end end # 頂点 class Vertex def initialize( id, data ) @id = id @data = data @edges = [] end def connect( to, weight ) @edges.push({ :to=> to, :weight=> weight }) end def disconnect( to ) @edges.reject! {|e| e.to === to } end def inspect return "#{@id}:#{@data.inspect}\n" + @edges.collect{|e| " -> #{e[:to]} : #{e[:weight]}" }.join("\n") end attr_reader :id, :data, :edges end
サンプルで使用するグラフは以下。
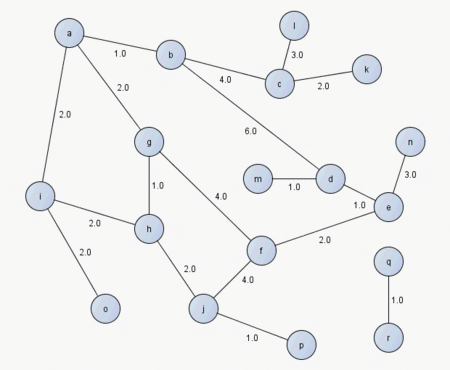
次のコードで生成できます。
graph = Graph.new ids = [] ('a'..'r').each{|i| ids << graph.add_vertex( i ) } graph.connect(ids[0], ids[1], 1.0) graph.connect(ids[0], ids[6], 2.0) graph.connect(ids[0], ids[8], 2.0) graph.connect(ids[1], ids[2], 4.0) graph.connect(ids[1], ids[3], 6.0) graph.connect(ids[2], ids[10], 2.0) graph.connect(ids[2], ids[11], 3.0) graph.connect(ids[3], ids[4], 1.0) graph.connect(ids[3], ids[12], 1.0) graph.connect(ids[4], ids[5], 2.0) graph.connect(ids[4], ids[13], 3.0) graph.connect(ids[5], ids[6], 4.0) graph.connect(ids[5], ids[9], 4.0) graph.connect(ids[6], ids[7], 1.0) graph.connect(ids[7], ids[8], 2.0) graph.connect(ids[7], ids[9], 2.0) graph.connect(ids[8], ids[14], 1.0) graph.connect(ids[9], ids[15], 1.0) graph.connect(ids[16], ids[17], 1.0)
ダイクストラ アルゴリズムによる最短経路探索の流れは以下のとおり。
- 開始位置から隣接する頂点を、最も軽い経路を優先して順に探索していきます。
- 例題の場合であれば、開始頂点である a の隣接頂点[b,g,i]をまず探索し、aからそれぞれの頂点までの重みを算出します。
- 算出した重み、および、前の頂点のIDは、最短経路の算出時に使用するため、頂点ごとに記憶しておきます。
- 次に、↑で探索された頂点のうち、最も短い=重みの合計値が低い経路である「b」の隣接頂点[c,d]を探索します。
- 最も短い経路を順に処理するため、優先度つきキューを使用します。
- bの探索が完了したら、次に軽い経路である「g or i」の隣接頂点を探索します。
- 以上を順に繰り返し、常に最も短い経路を優先してすべての経路を探索していきます。
- 例題の場合であれば、開始頂点である a の隣接頂点[b,g,i]をまず探索し、aからそれぞれの頂点までの重みを算出します。
- すでに探索済みの頂点に別のルートで再度到達した場合、より短い方の経路を採用し、記憶されている算出した重みと前の頂点のIDを更新します。
- 開始位置から到達可能なすべての頂点を探索すれば、処理はそこで終了。
- 目的の頂点に到達しても、他の経路のほうが短い可能性があるため、すべての経路の探索が完了するまで処理は継続されます。
実装は次のような感じになります。優先度つきキューの実装はpriority-queueを使用しました。
require 'graph' require 'priority_queue' # ダイクストラ アルゴリズムでノード間の最短経路を算出する class ShortestPathFinder def initialize( graph ) @graph = graph end # startからすべてのノードへの最短経路を探索する def traverse( start ) initialize_state( start ) @queue.push( start, 0 ) while( vertex_id_and_distance = @queue.delete_min ) visit_vertex(vertex_id_and_distance[0], vertex_id_and_distance[1]) end return self end # 指定頂点までの最短パスを構築する。 def shortest_path_to( vertex_id ) raise "not traversed" unless @start path = [] while( @previous.include?( vertex_id ) && vertex_id != @start ) path.unshift(vertex_id) vertex_id = @previous[vertex_id] end return path end private # 状態を初期化する def initialize_state(start) @queue = PriorityQueue.new @distances = {} @previous = {} @start = start end # 頂点を訪問する def visit_vertex( vertex_id, distance ) @graph.vertices[vertex_id].edges.each {|e| to = e[:to] distance_of_next_node = distance + e[:weight] if ( not_visited_or_shorter_path?( to, distance_of_next_node ) ) @previous[to] = vertex_id @distances[to] = distance_of_next_node @queue[to] = distance_of_next_node end } end # 訪問済みでない、またはより短いパスであるか評価する。 def not_visited_or_shorter_path?( vertex_id, distance ) return !@distances.include?(vertex_id) || @distances[vertex_id] > distance end end
利用例。graph は↑で作成したものです。
finder = ShortestPathFinder.new( graph ).traverse(ids[0]) graph.vertices.each {|v| path = finder.shortest_path_to(v.id).collect{|id| graph.vertices[id].data }.join(' -> ') puts "#{v.data} : #{ path }" }
実行結果です。到達不能なq,rのパスは空配列になります。
a : b : b c : b -> c d : b -> d e : g -> f -> e f : g -> f g : g h : g -> h i : i j : g -> h -> j k : b -> c -> k l : b -> c -> l m : b -> d -> m n : g -> f -> e -> n o : i -> o p : g -> h -> j -> p q : r :

